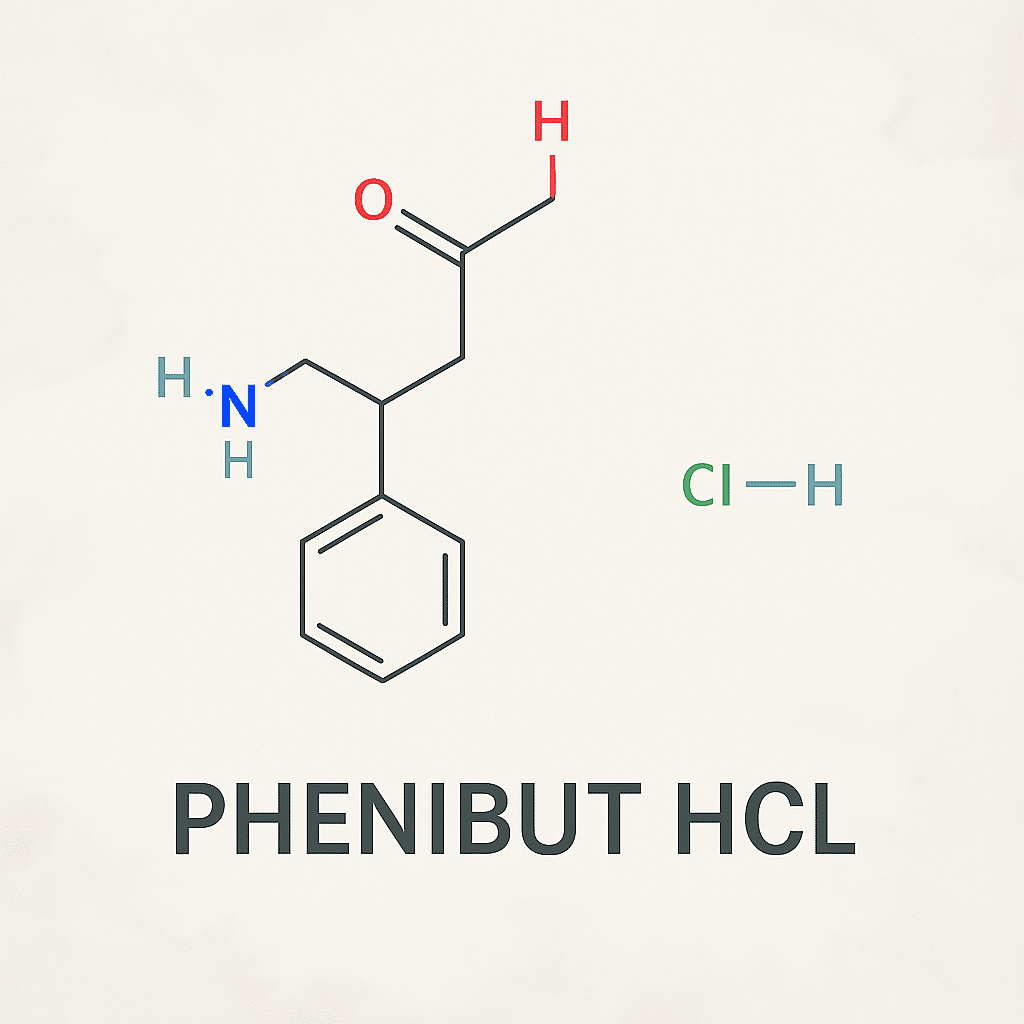
Phenibut HCL
10,00 € – 33,00 €Plage de prix : 10,00 € à 33,00 €
Note: For research and educational purposes only. Not intended for human consumption.
Phenibut is a nootropic compound originally developed in Russia, known for its calming and mood-enhancing properties. It supports relaxation, promotes restful sleep, and may help reduce feelings of stress and social anxiety. Popular among those seeking a balanced mind and body, Phenibut offers a unique blend of focus and tranquility.
i) The Pharmacology of Phenibut
✅ Primary Mechanism of Action:
GABA-B Receptor Agonist
- Phenibut is structurally similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but is able to cross the blood-brain barrier due to its phenyl ring.
- It primarily acts as a GABA-B receptor agonist, producing anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), sedative, and calming effects.
- GABA-B receptor activation reduces neuronal excitability, leading to relaxation and a decrease in stress response.
✅ Secondary Actions / Additional Pharmacology:
GABA-A Receptor (Weak Action):
- There is limited evidence that Phenibut may have minor activity at GABA-A receptors, but this is not its main pathway and is significantly weaker compared to GABA-B interaction.
Dopamine Modulation:
- Phenibut increases dopamine levels in certain brain regions, particularly the striatum and nucleus accumbens.
- This dopaminergic effect may contribute to its mood-enhancing, pro-social, and mild euphoriant effects.
Calcium Channel Effects (Possible):
- Some research suggests Phenibut may interact with voltage-gated calcium channels, similar to how baclofen (a GABA-B agonist) acts, though this is not well-documented in humans.
✅ Summary of Neurotransmitter Systems Affected:
| System | Action | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| GABA-B | Agonist | Anxiolytic, calming, sedative |
| GABA-A | Weak/Minimal action | Mild influence on relaxation |
| Dopamine | Indirect increase (release/modulate) | Mood elevation, pro-social |
| Calcium Channels | Possible modulation | Further CNS depressant effects |
ii) Phenibut Dosing Overview
Phenibut has a narrow therapeutic window, and responsible use is crucial to avoid tolerance or dependence.
✅ Common Dosage Range:
- Light: 250–500 mg
- Moderate: 500–1000 mg
- Strong: 1000–1500 mg
Note: New users should start low to assess individual sensitivity.
✅ Onset & Duration:
- Onset: 2–4 hours (slow acting)
- Peak: 4–6 hours
- Duration: 12–24 hours (effects can linger the next day)
iii) ⚠️ Important Considerations & Warnings
🚫 Risk of Tolerance & Dependence
- Regular use (even 2-3 times per week) can lead to rapid tolerance buildup.
- Phenibut is habit-forming due to its action on the GABA-B system.
- Recommended use: No more than 1-2 times per week to minimize risks.
⏳ Withdrawal Risk
- Daily use or high doses can lead to withdrawal symptoms: anxiety, insomnia, agitation, and in severe cases, seizures.
- Gradual tapering is required if used regularly over time.
❌ Interactions
- Do not combine with alcohol, benzodiazepines, or other central nervous system depressants. This can lead to dangerous sedation, respiratory depression, or blackouts.
- Caution with other GABAergic or sedating substances.
🧠 Cognitive Impact
- While low doses may promote focus and sociability, high doses can impair coordination, memory, and cognition.
- “Next-day grogginess” is common with higher doses.
| Συσκευασία |
10 g. ,20 g. ,50 g. |
|---|
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS :
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Phenibut HCL |
| CAS Number | 1078-21-3 |
| Chemical Formula | C10H13NO2 |
| Grade | Medical grade |
| Purity | 99% |
| Test Method | HPLC |
Ideal storage is done in a cool and dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat. Has to be labeled clearly at all times and be kept out of reach of children!
WHAT TO AVOID :
- Benzodiazepines
- Alcohol
- GABAergic compounds (Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Baclofen)
- Opioids / Opiates
- Sleep aids / Sedatives
- Muscle relaxants
- High doses of stimulants
DISCLAIMER :
As stated in the short description, this and other products of subsection of
“Nootropics” in our e-shop are NOT intended for human consumption! Those products are available for collection purposes or for other lawful use for which the consumer has taken care to be explicitly informed on a personal level in every aspect that may be affecting them.
The information provided in the descriptions of products which can be found in “Nootropics” subsection – as available from ethosherbals.com, SMARTSHOP Main Category – is of an academic nature. This information is not intended to be used for human consumption of the products in question. It is not intended to diagnose, prevent or treat any medical condition. It is not intended to be a substitute for any medical treatment.
Vous devez être connecté pour publier un avis.









 Ethos Herbals Blends
Ethos Herbals Blends Κάνναβη
Κάνναβη SmartShop
SmartShop VapeShop
VapeShop Θεραπευτικά Βότανα
Θεραπευτικά Βότανα Κακάο & Τσάι
Κακάο & Τσάι Αρωματοθεραπεία
Αρωματοθεραπεία Ethos Lifestyle
Ethos Lifestyle
Avis
Il n’y a pas encore d’avis.